Practice Leads
- Doctors: Jaz Dhilon
- Nurse: Jo Young
Date Reviewed
14 April 2016
Date of Next Review
September 2017
Definitions
The care BEFORE someone has given birth is called ‘ANTEnatal care’. The care AFTER birth is referred to as ‘POSTnatal care’.
What happens when a patient tells the doctor they are pregnant?
All routine pregnancies will follow this procedure – the care plan for non-routine pregnancy will be decided between the Midwife/GP/hospital and patient as need dictates.
- A patient who thinks they are pregnant should do a pregnancy test (which are cheap and available from all pharmacies). Pregnancy tests purchased from a pharmacist are very reliable. If the pregnancy test is positive, the patient needs to come and see their GP.
- Then the patient needs to come in and see the GP. The GP may need to confirm pregnancy test. The GP will ask relevant clinical questions. The GP will then refer to Midwife via appropriate referral form. An indication of the chosen hospital to be cared under will be discussed and written down. Relevant pregnancy advice will be given. The pregnant patient will need to start taking Folic Acid tablets (also available from pharmacies) for the first 12 weeks of pregnancy.
- The patient will be sent information regarding antenatal screening and a ‘booking in’ first antenatal appointment. This is usually between 8 – 12 weeks gestation.
- Thereafter, follow-on visits occur in accordance with the local hospital’s guidelines & NICE.
- A scan is offered at 20 weeks gestation.
Actions for Admin Staff – when a patient fails to keep an appointment (DNA)
- 1st DNA for Hospital Booking Appointment – Receptionist checks with GP surgery regarding patient still pregnant then further appointment forwarded for one week – by post.
- 2nd DNA for Hospital Booking Appointment – Community Midwife informed and appointment left ‘open’ until Community Midwife contacts Antenatal Clinic regarding further appointment. Medical staff write to GP and Midwife.
- DNA at 20 weeks detailed scan appointment – action as above
- All other DNAs – checked by Midwife in Charge. Patient contacted if possible, Medical Staff informed. If unable to contact patient directly, Community Midwife asked to visit and inform Antenatal Clinic regarding further appointment visit as necessary.
- Above guidelines are flexible – each patient assessed individually.
Antenatal schedule (including scan date)
- booking in appointment – at around 11 weeks – midwife explains things about pregnancy, and initial plans made regarding antenatal care & the birth.
- 20 weeks – you will have an Ultrasound Scan to make sure your baby is fine.
- 24 weeks – you will receive a general check up
- 28 weeks – check up, blood testing and antibody screening
- 31 weeks – check up
- 34 weeks – check up, MRSA screening offered
- 36 weeks – check up, blood testing and care/birth plan discussion
- 38 weeks – check up
- term (40 weeks) – check up. Discussion re post maturity 41 weeks apt made for stretch & sweep or follow up at hospital.
If any problems arise, you will be seen more regularly and/or referred to the Woman & Newborn Unit at BRI.
Postnatal schedule
- After delivery, women are visited by the Community Midwives who may also involve the GP if this is necessary.
- During the second week after delivery, the Health Visitor will continue to support you and baby.
- You will be invited for a post-natal appointment after six weeks to see one of the GPs. They will check to make sure you are okay and discuss your plans for future contraception if appropriate.
Routine Blood Samples for Antenatal Care
| 1 | Blood Grouping | All patients on first visit |
| 2 | Rhesus Negative | Sample required on first visitRepeated at 28+weeks(also repeated at time of delivery) |
| Rhesus Positive Patient with history of blood transfusion | Further samples to be obtained at the request of the Blood Transfusion Service | |
| Antibody Serology | All patients (Rh positive or negative) at first visit and repeated at 28 weeks & 36 weeks.The Rhesus Negative patient must also have sample taken at 28 weeks | |
| 3 | Full Blood Count | First visit, and repeated as indicated |
| 4 | Rubella Antibody Titre | First visit only. (repeat as requested by laboratory or if patient has been in contact with Rubella)This test should be repeated in each pregnancy |
| 5 | Down’s Risk Screening | Offered to all patients – combined screening, see guidelines @ BHFT. |
| 6 | HIV/Hep B | Offered to all patients at first visitThis test should be repeated in each pregnancy |
Special tests that may be required
| 1 | Sickle Cell | Test for specific type of hereditary anaemia usually of relevance to people of African or Caribbean origin |
| 2 | Thalassaemia | Test for another hereditary anaemia affecting some people of Mediterranean origin |
| 3 | Hepatitis C | Offered as part of booking process. |
| 4 | Toxoplasmosis | No evidence that screening is beneficial |
| 5 | Blood Glucose Levels | Refer to the current policy on screening for gestational diabetes |
| 6 | Rubella Antibodies | Offered as part of booking process. |
| NB: Reasons for not adhering to these guidelines must be documented in the patient’s medical records | ||
What happens when and with whom?
| Gestation Weeks | WHO WITH | APPOINTMENT | 1st Pregnancy | More Pregnancy |
| 8-12 | Community Midwife/Hospital Midwife | 1 hour booking appointment./ Screening offered, including bloods, urinalysis, weight, height and blood pressure | √ | √ |
| 11-14 | Scan Dept at Hospital | Combined Screening appointment offeredOr dating scan offered | √ | √ |
| 16 | Community Midwife/Consultant at Hospital | Antenatal review /Chlamydia screening for under 25s | √ | √ |
| 18-22 | Scan Dept at Hospital | Fetal normality scan | √ | √ |
| 25 | Community Midwife/Hospital Doctor | Antenatal review / MAT B1 form | √ | X |
| 26 | Hospital | Glucose Tolerance test offered | √ | √ |
| 28 | Community Midwife/Hospital Doctor | Antenatal review /Repeat bloods/Anti D if Rhesus Negative | √ | √ |
| 31 | Community Midwife/Hospital Doctor | Antenatal review / Sure Start grant form signed if required | √ | X |
| 34 | Community Midwife/Hospital Doctor | Antenatal review and discuss birth planMRSA screening offered | √ | √ |
| 36 | Community Midwife/Hospital Doctor | Antenatal review / bloods taken /weight / 36 week pack | √ | √ |
| 38 | Community Midwife/Hospital Doctor | Antenatal review / book post date appointments | √ | √ |
| 40 | Community Midwife/Hospital Doctor | Antenatal review | √ | √ |
| 41 | Community Midwife/Hospital Doctor | Offer Stretch and sweep / book induction | √ | √ |
————————————————
- MAT B1 certificate can be issuesd from 20 weeks gestation
- Current evidence suggests that serial weighting is no longer appropriate in routine antenatal care. Please do however continue to weigh at booking and in late pregnancy.
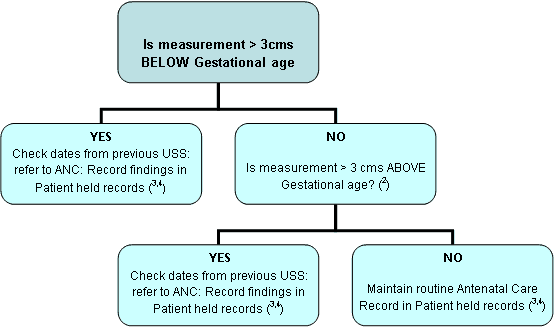
- It is requested that fundal height measurements are undertaken routinely at all antenatal checks after and including 26 weeks. Deviation of more than 3 cms outside the gestational age should be referred for ultrasound assessment (Calvert et al 1982)
Fundal Height Checks – guidance for GPs
Definition: Measurement of the abdomen taken from the upper border of the pubic symphysis to the uterine fundus[i]
Aim: To be used as an indicator for predicting both low birth weight for gestation babies and signs of polyhydramnios. This is used as a screening indicator[ii]
Procedure
- At 26 week gestation and above, Symphysis – Fundal Height should be measured and then at each routine antenatal examination subsequently.
- Fundal height should be measured number side down on the tape, from the fundus to the upper border of the Symphysis pubis. (The measurement is more viable if the same person performs the examination at each visit)
- The measurement carried out from 26 weeks gestation should in cms be approximate to the gestational age e.g. 35 weeks gestation should measure 35 cms 1,2
- Lindhard et al – the implications of introducing symphyseal – Fundal height measurement. A prospective randomised controlled trial. British Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology (1990) 97:675-680
- Altman et al – Assessment of Foetal Size and Foetal Growth. Effective Care in Pregnancy and Childbirth. OxfordUniversitypress (1981) 511-418
- James DK et al – An Obstetrics and Gynaecology Vade-Mecum (2000) Oxford University Press p13
- UKCC Midwives Rules: Rule 40, 42